A solar eclipse takes place when the sun, moon, and earth align in such a way that the moon is between the sun and the earth and the sun is partially or fully obscured by the moon. This obscurement of the sun is only visible at places where the moon’s shadow falls. A solar eclipse can only occur during the new moon phase of the moon and during an eclipse season.
(The new moon is that phase of the moon when the lunar disk is not visible to the naked eye.)
Types of Solar Eclipse
Total solar eclipse
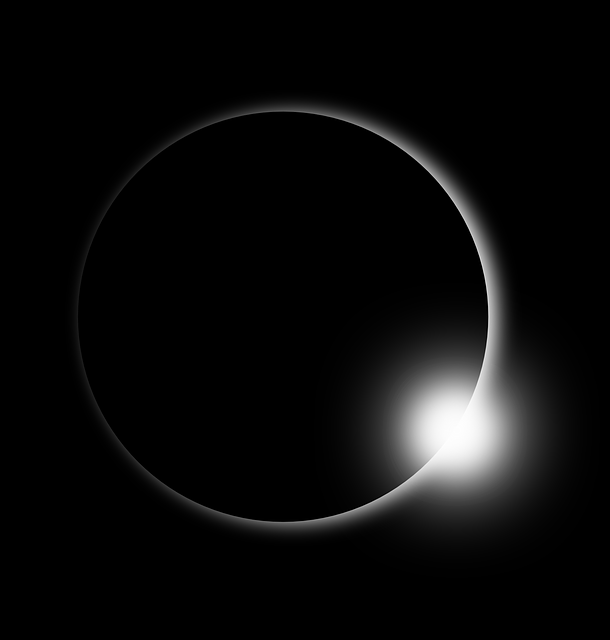

A total eclipse takes place when the moon covers the sun completely. The places where the darkest part of the moon’s shadow (umbra) falls witness a total solar eclipse, while the places where the fainter shadow (penumbra) falls witness a partial solar eclipse.
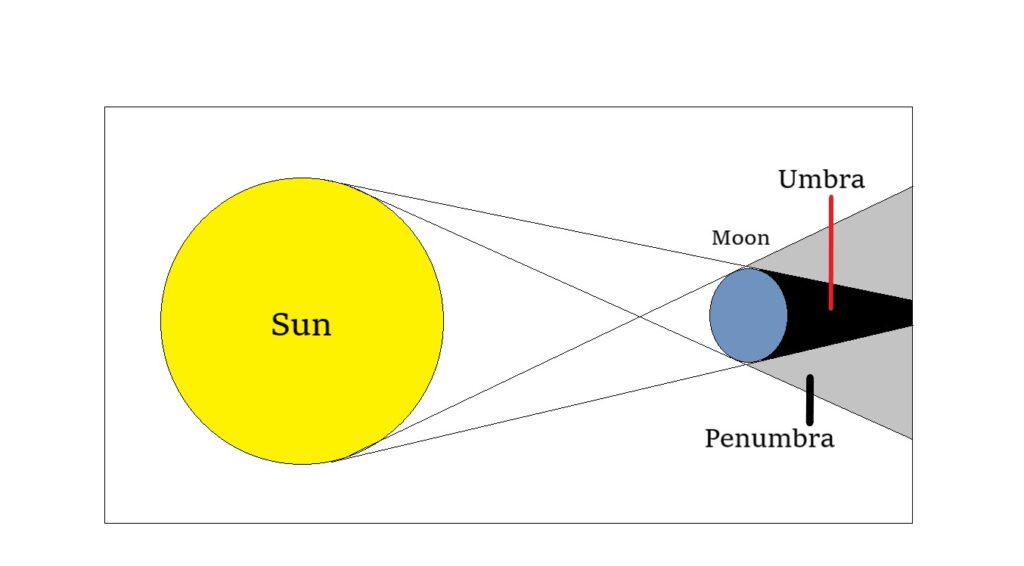
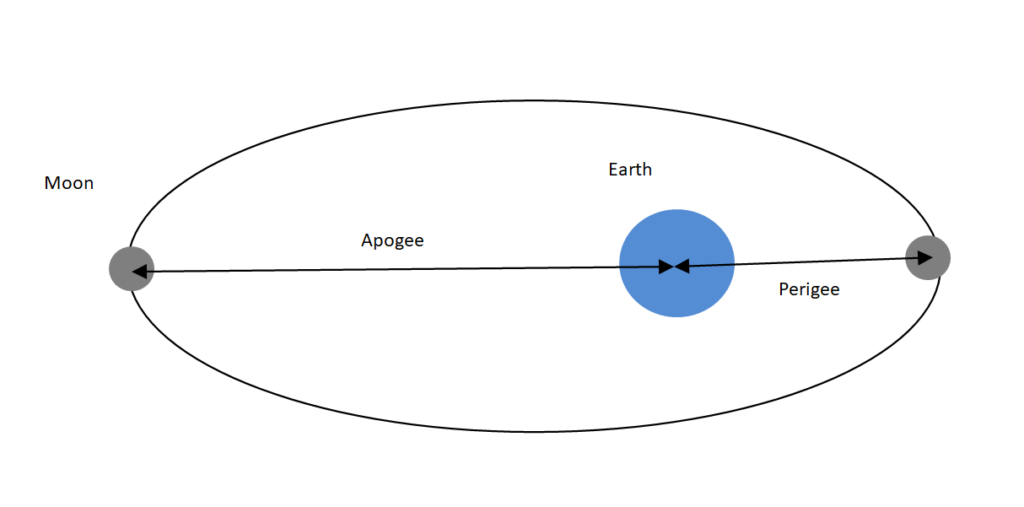
A total solar eclipse is visible only along a narrow path on Earth known as the path of totality. This type of eclipse occurs when the moon is near the perigee, i.e., closest to the Earth. During a total eclipse, we get to witness the sun’s corona, the outer plasma layer of the sun.
Disclaimer: Do not watch solar eclipses with naked eyes, you may permanently lose your eyesight.
Partial solar eclipse
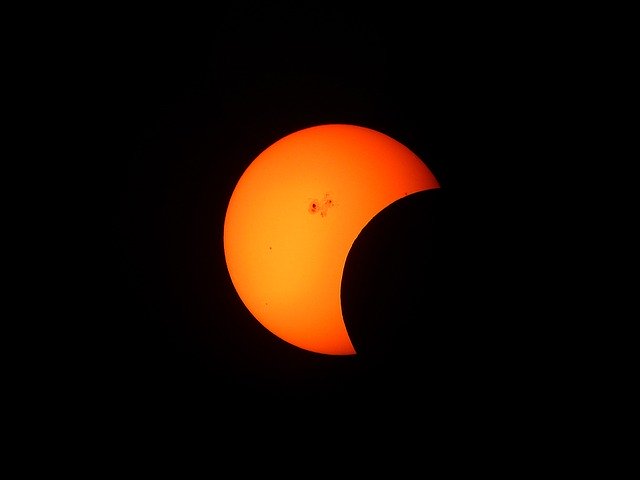

A partial eclipse occurs when only a part of the sun is obscured by the moon. It occurs at places where penumbra falls. If an eclipse is stated as partial, then the umbra will miss the Earth, and no place will witness a total solar eclipse. While if an eclipse is stated as total or annular, then a partial solar eclipse will also occur at places where penumbra falls.
Annular solar eclipse
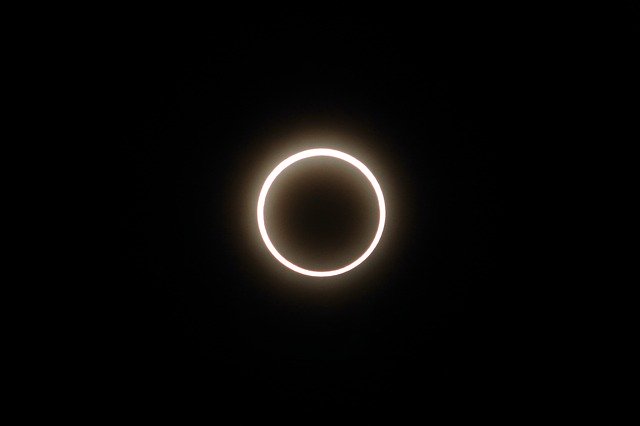

An annular eclipse takes place when the moon is not able to cover the sun completely. An annular ring of fire is visible around the moon. This type of eclipse occurs when the moon is near its apogee i.e., farthest from the Earth.
(Also read: Top 10 brightest objects in the night sky)
Hybrid solar eclipses
These are rare eclipses, also known as annular-total eclipses. During these eclipses, an annular eclipse changes to total and then again changes to annular along the path of the eclipse. This happens due to the curvature of the Earth.
Eclipse season
Eclipse season is the time period when the Earth, Sun, and Moon can align in a straight or near straight line to cause an eclipse (lunar or solar). Each eclipse season lasts for about 35 days and repeats in a little less than 6 months. There can be 2 to 3 eclipses in one eclipse season and 2 to 5 eclipses in a calendar year.
The moon’s orbital plane is tilted at an angle of about 5 degrees with respect to Earth’s orbital plane (ecliptic). That’s why eclipses do not occur every month.
Eclipse future
The moon is moving away from the earth at a pace of about 4 cm per year. Currently, the moon is about 1/400 times as far away as the sun is from the earth. Also, the sun is approximately 400 times bigger in diameter than the moon. Hence, both the sun and the moon appear to be the same size in the sky. However, this will not be the case in the future, and there will be no total eclipses.
(The moon’s orbit will reach its maximum size at some point in the future, then it will start to shrink. The moon will probably never leave Earth.)
Next eclipse
The next solar eclipse is on 8 April 2024. It will be a total eclipse.
Quick question
Which is the second brightest object in the night sky after the moon?
Read more
- Mars facts – orbit, physical overview, natural satellites, etc.
- Ganymede, the largest moon of the solar system | Top 5 largest moons
Answer to quick question
Venus is the second brightest object in the night sky after the moon. Venus also has different phases just like the moon.