There are 4 main types of mountains/mountain ranges classified on the basis of the process of formation.
- Fold mountains
- Block mountains
- Volcanic mountains
- Residual mountains
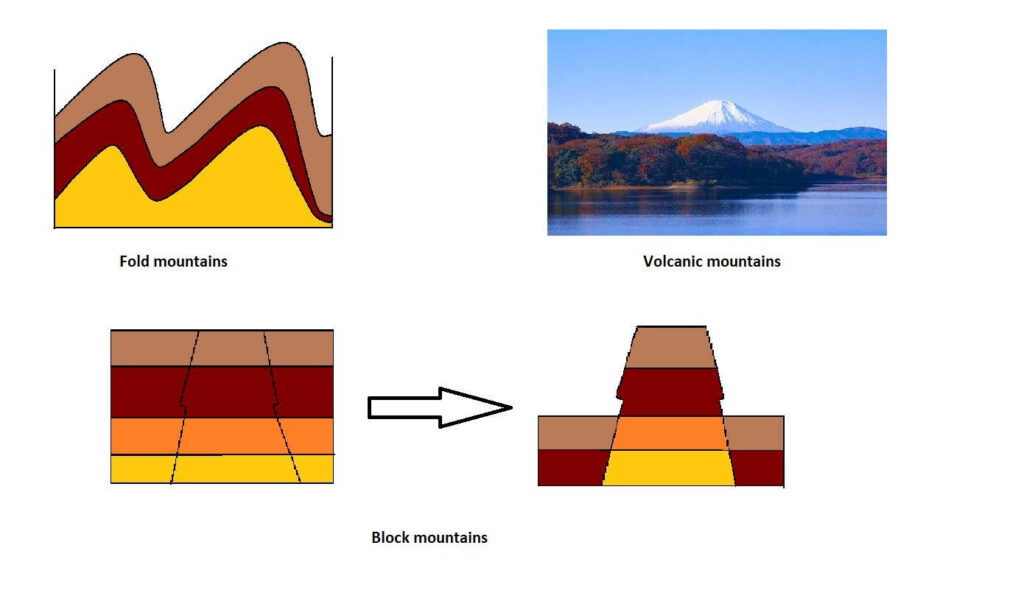
Types of mountains
Fold mountains
These are the most common type of mountains. Nearly all the famous mountain ranges e.g. the Himalayas, the Alps are fold mountains. Fold mountains form when two tectonic plates collide along the convergent boundary.
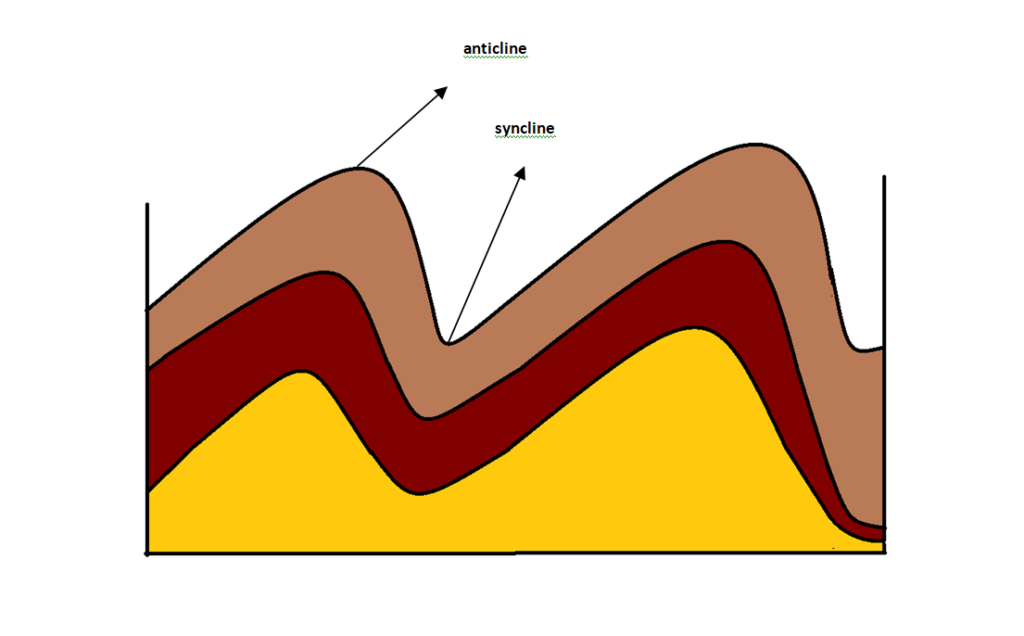
The collision creates numerous folds in the Earth’s crust. The folds resemble the wrinkles of a tablecloth. The upfolds are known as anticlines whereas the downfolds are known as synclines.
Volcanic mountains
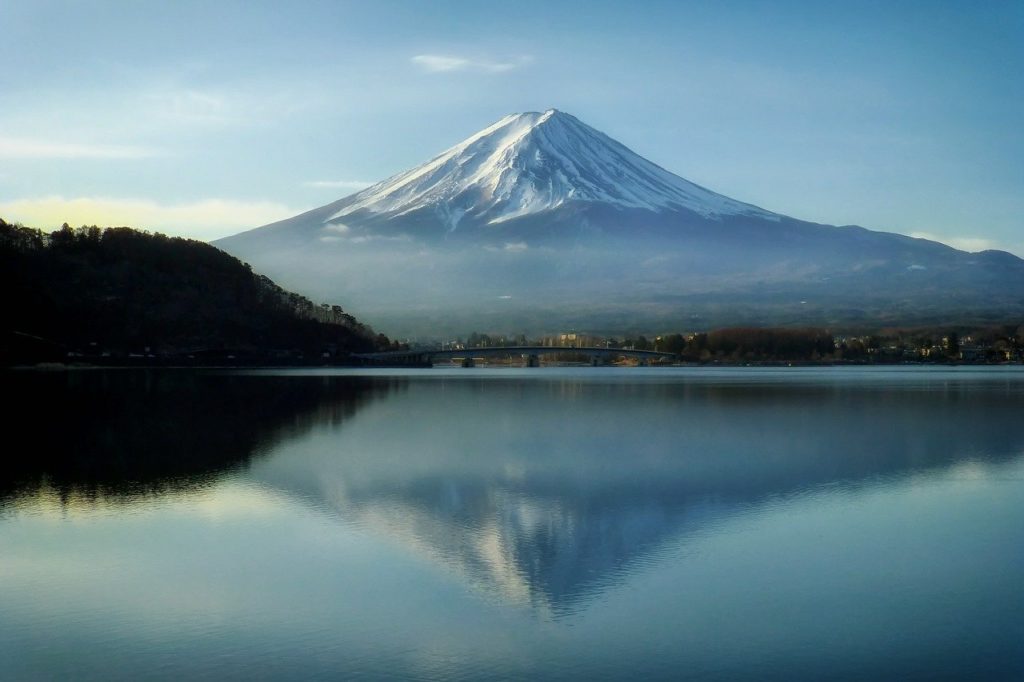
Volcanic mountains are formed from the lava and tephra that come out of a volcanic vent. These mountains are stratovolcanoes whose size increases after each eruption.
The lava that comes out of the stratovolcanoes is highly viscous. It does not travel far and starts solidifying near the vent. Slowly a mountain develops around the vent. Each eruption adds a new layer to the slopes of the mountain. Mount Fuji in Japan is a classic example of a volcanic mountain.

Block mountains
Block mountains form due to the faults created in the Earth’s crust by the tension and compression forces. The tension forces pull the crust creating faults. If the block between the two faults does not subside while the crust on either side of the block subsides, a block mountain is formed.
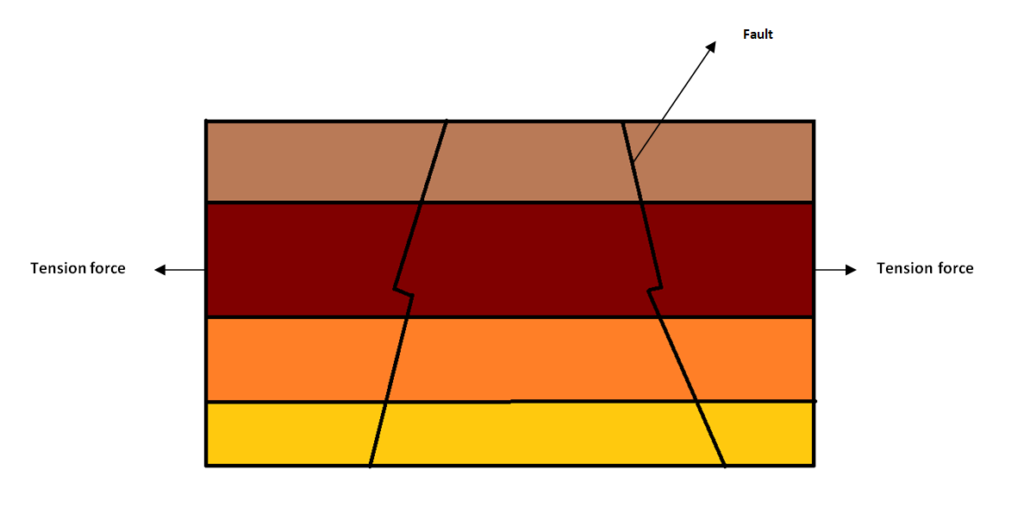
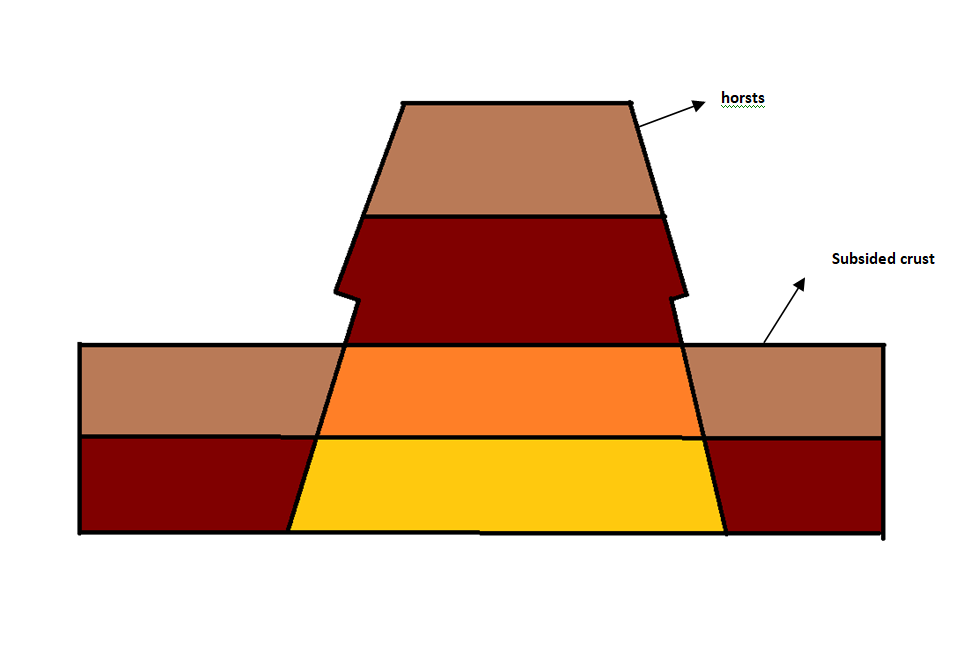
Compression forces on the other hand create rift valleys or graben.
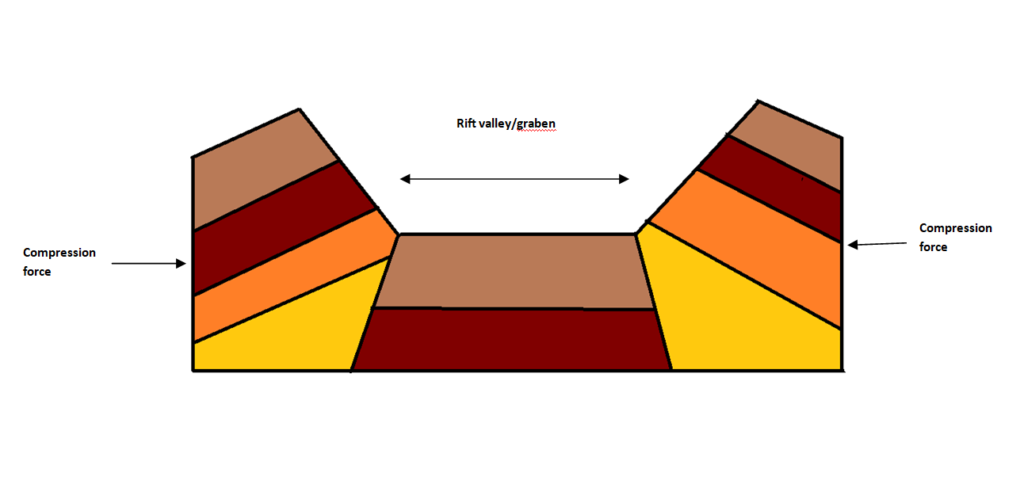
Rift valleys also form between two horsts.
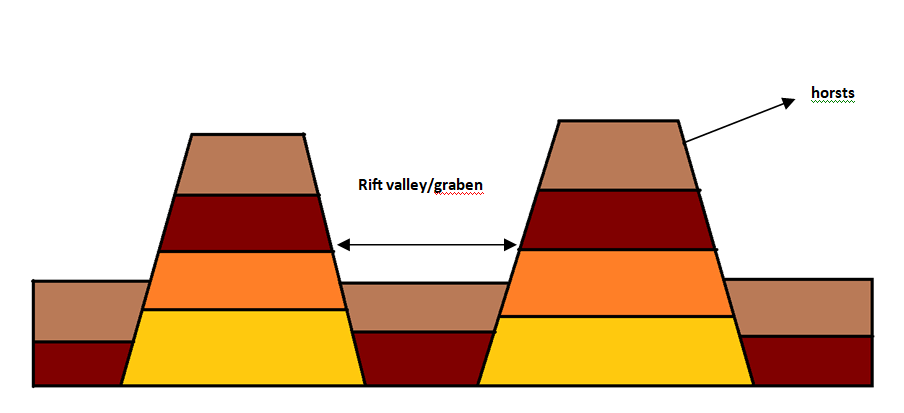
Residual mountain
Residual mountains form after years of denudation of the Earth’s crust by the wind, moving water, erosion, weathering, etc. Pieces of land hard enough to resist denidation transform into residual mountains. Mount Monadnock in the USA is an example of a residual mountain.
Quick question
Which is the second-highest mountain peak in the world (above sea level)?
Read more
- Major mountain ranges in the world
- Types of volcanoes | Some infamous volcanic eruptions
- Highest mountains in the world – the eight-thousanders
Answer to quick question
K2 is the second-highest peak in the world. Kanchenjunga is the third highest.