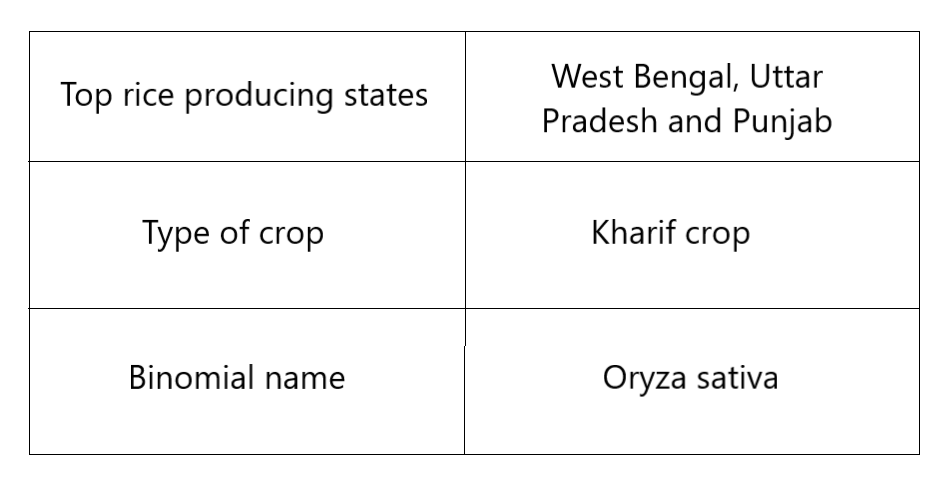
Rice is the most cultivated crop in India. The total annual production was around 136 million MT for 2022-23 season. Rice is primarily a Kharif crop sown in the summer and harvested from late October to December. In most of eastern and southern India, rice can grow throughout the year due to favourable climate.

Just like Wheat, Rice is also grass. It is one of the oldest cultivated crops in the world. Although, its origin is still debated. Some scholars believe rice was first cultivated in India while some think southern China is the place where rice cultivation first started.
Rice grows best in hot and humid conditions and requires plenty of water. As rice is mostly sown during the summers in India, the monsoon rains that follow provide the required water for growth. The optimum temperature for the growth is 20-35 degrees Celsius.
West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, and Punjab are the largest rice-producing states in India. India overall is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China. India is also the largest exporter of rice in the world.
Rice can grow in almost every Indian soil. The growth period depends on the variety but on average is 105-120 days. The average yield is 20-30 quintals per hectare.
Since rice is a major crop in India, a wide range of varieties have developed over time. The most consumed varieties are Basmati, white rice, and Brown rice. The consumption of rice is more in southern and eastern India as compared to North India where wheat is the major cereal crop. In the North, rice is generally eaten with pulses or beans.
India is already leading the world in rice production. However, there is still a lot of potential to increase production. The average yield per hectare is much lower than in other rice-producing countries like China and Indonesia. With the advancements in farming techniques, India can overtake China in total rice production.
Read more