Tides are the rise and fall of the ocean level. The gravitational pull of the sun and the moon, and the rotation of the earth are the two causes of tides. Let’s learn about the different types of tides.
Types of tides
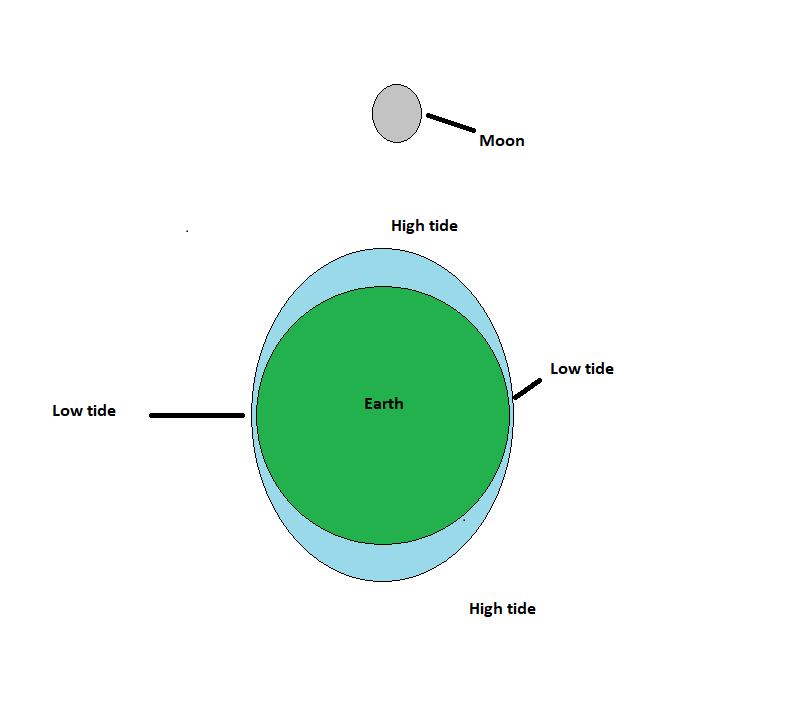
Places on earth that are closest to the moon at a given point in time experience a high tide. During a high tide, the ocean level rises and the water moves up on the shore to the maximum extent.

The moon exerts the gravitational force which pulls the water up causing high tides. The places which do not face the moon experience a low tide. During a low tide, the water recedes from the shore.

The side of the Earth opposite to the side facing the moon also experiences a high tide. This is because of the centrifugal force generated due to the rotation of the earth. The water accumulates on this side of the earth causing a high tide.
What is tidal range?
The tidal range is the height difference between high tide and low tide.
1. Types of tides based on frequency
Diurnal, Semidiurnal and Mixed tides
There are generally two high tides and two low tides each day in most parts of the world. When the two high tides (also the two low tides) have roughly the same height, the tides are known as semidiurnal tides. When the two high and two low tides per day have unequal heights, the tides are known as mixed semidiurnal tides.
Due to the geography of the earth, there is only a single high tide and a single low tide during the day in some areas. The tides in these areas are known as diurnal tides.
2. Types of tides based on alignment of Sun, Moon, and the Earth
Spring and Neap tides
Spring tides occur during the new moon or the full moon. During a spring tide, the gravitational pull of the moon and sun add up to create a tidal range greater than usual.
(New moon occurs when the moon is between the sun and the earth. Full moon occurs when the earth is between the sun and the moon.)
Neap tides occur when the direction of the moon is perpendicular to the direction of the sun. This results in tides with a smaller range.
(Also read: The different phases of the moon | Why the moon has phases?)
3. Other
Tidal bore
A tidal bore is a phenomenon in which the incoming tide forms a wave that travels up a narrow river or estuary, against the direction of the river current.
Perigean and Apogean tides
Perigean tides occur when the moon is closest to earth (at perigee), increasing its gravitational effect and causing higher high tides and lower low tides.
Apogean tides occur when the moon is farthest from earth (at apogee), resulting in lower high tides and higher low tides.
Perigean spring tide
A perigean spring tide is a spring tide that occurs when the moon is closest to earth, i.e. at perigee.
Apogean neap tide
An apogean neap tide is a neap tide that occurs when the moon is at the farthest point from Earth (apogee) in its orbit.