The sky in the day appears blue. Why do we only see the different shades of blue and not the other colors? Why the sun appear reddish during sunrise and sunset and yellowish during the day? All these things can be explained by just one phenomenon. What is that? Let’s find out.
Why is the sky blue?
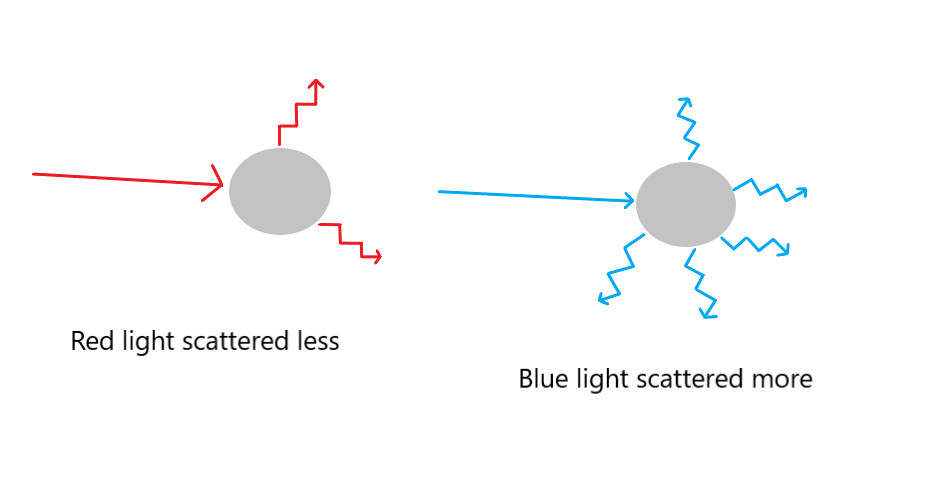
The sky appears blue in color because of the scattering of sunlight. The white sunlight is actually composed of seven different colored lights (Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red). The sunlight is scattered by the air molecules in the atmosphere. This scattering is governed by the following formula (Rayleigh scattering).
Intensity of scattering of light ∝ 1/(λ^4)
where λ is the wavelength of the light
The intensity of scattering will be higher if the wavelength of the light is low. The violet-colored light, which has the lowest wavelength, is scattered the most, while the red-colored light is least scattered.
Blue light is the third most scattered light. Since the concentration of blue light is higher in the sunlight than violet and indigo. Also, our eyes are more sensitive to the blue color. That’s why the sky appears blue.
Why the Sun appears reddish during sunrise and sunset and yellowish during the day?
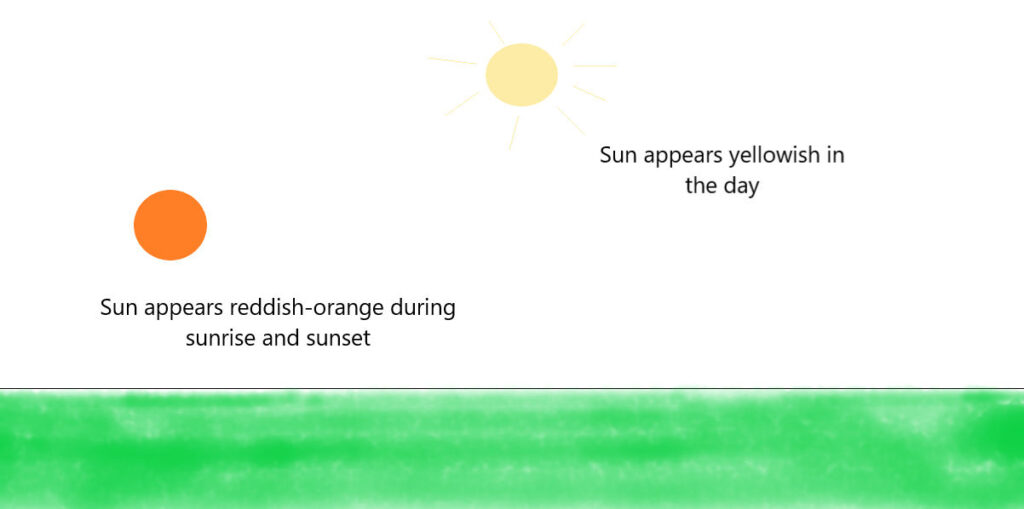
In the day, the sun appears yellowish because the violet, indigo and blue lights are scattered away. With a lack of blue, Sun appears yellowish.
During sunrise and sunset, the sun is near the horizon, and the sunlight has to travel through more atmosphere. The sun appears reddish-orange as more scattering takes place of other lower wavelength lights.
Other examples of scattering of light
Red colour danger signals
The danger signals and stop signals are always red, as the red color is the least scattered. The red color can be seen from the farthest distance.
The white colour of the clouds
Clouds are made up of water droplets that are much bigger than air molecules. These droplets scatter all the lights in equal proportions. The clouds thus appear white.
Read more