A tropical cyclone (hurricane) is a large storm system comprising high-speed winds and thunderstorm clouds that rotates around a low-pressure area known as the eye of the cyclone. Tropical cyclones rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
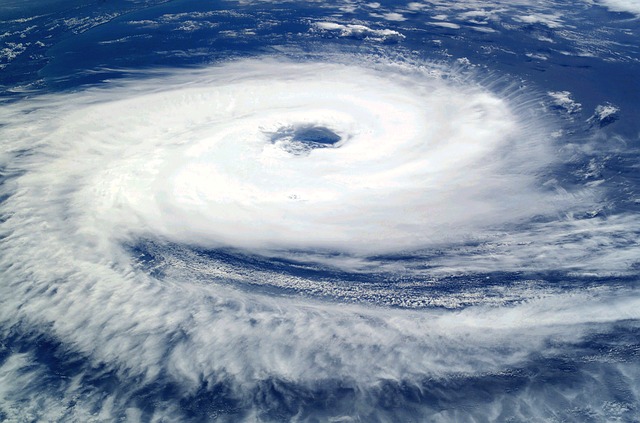

Tropical cyclone, hurricane, typhoon, and willy willies are all different names for the same kind of storm. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean, these storms are known as cyclones. They are known as hurricanes in North Atlantic and Northeast Pacific countries; typhoons in the North West Pacific countries; and willy willies in Western Australia.
Things to learn before understanding cyclone formation
1. Coriolis force
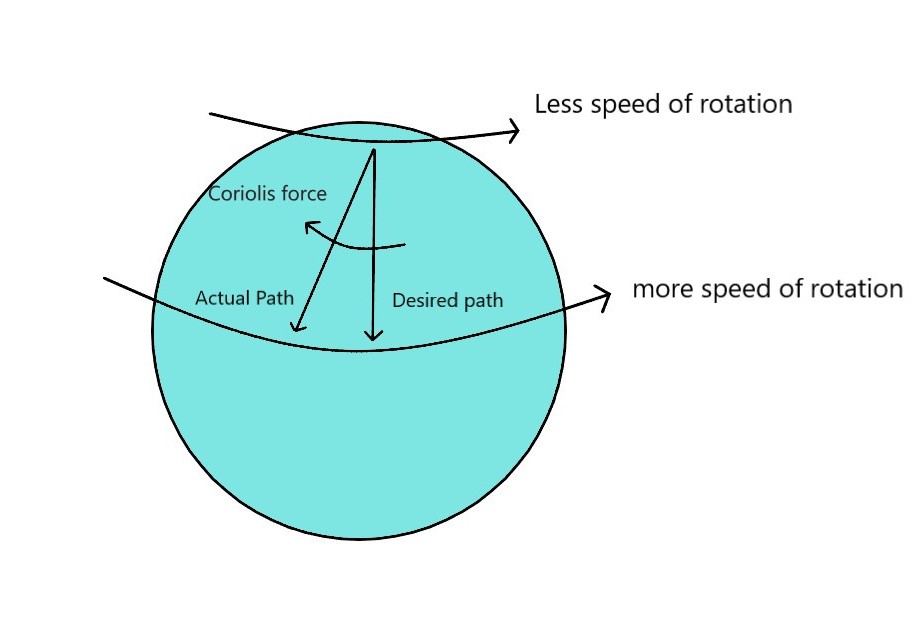
It is an inertial force that acts on objects moving up or down the latitudes in the Northern or Southern Hemisphere. As we know the Earth rotates at a faster speed at the equator and at a slower speed at the poles. If an object tries to move from the North pole towards the equator in a straight line without being attached to the ground, it will land right of the desired destination.
Similarly, if an object tries to move from the equator towards the North Pole in a straight line without being attached to the ground, it will again land right of the desired destination.
2. Air movement based on pressure
Air or wind moves from a high-pressure area to a low-pressure area.
3. Air movement based on temperature
Warm air rises and cool air sinks.
Requirements for a cyclone formation
- Surface ocean water temperature of more than 26 degrees Celsius and water depth of more than 50 m.
- The atmospheric temperature must dip sufficiently with height to support the formation of clouds.
- A preexisting low-level disturbance near the warm ocean water.
- The wind speeds must not change too much with height i.e. vertical wind shear must be less.
Formation of a tropical cyclone
When the warm ocean water near the equator (above 26 degrees Celsius) evaporates, it makes the air above the water surface warm and moist. This warm, moist air then rises, creating a low-pressure area below it.
As we know air moves from an area of high pressure to low pressure. Air from surrounding areas rushes towards the low-pressure area where it becomes warm and moist and consequently rises creating a cycle.
The air rushing in starts rotating because of the Coriolis force. The rising moist air cools as it gains elevation and hence clouds are formed. These winds and clouds together rotate giving rise to the cyclone. These cyclones are known to reach diameters above 300 km.
In the Northern Hemisphere, the cyclones rotate counterclockwise and in the Southern Hemisphere, they rotate clockwise. The eye is relatively calm.
(Also read: Countries through which the equator passes)
Landfall
When cyclones reach a coast, it is known as landfall. The wind speeds slow down upon landfall as there is no warm ocean water to fuel the cyclone. In general, cyclones die down when they make landfall or when they reach cold waters. Landfall can cause extreme damage to life and property.
Read more
hmmm🤔🤔🤔